Entrepreneurship
January 2026 at Marico Innovation Foundation: The year picks up pace
Milestones, lessons, and the work already underway at MIF
Rural women entrepreneurs face significant systemic hurdles, but with skills, capital, mentorship, and societal shifts, they can drive rural India's economy and well-being.
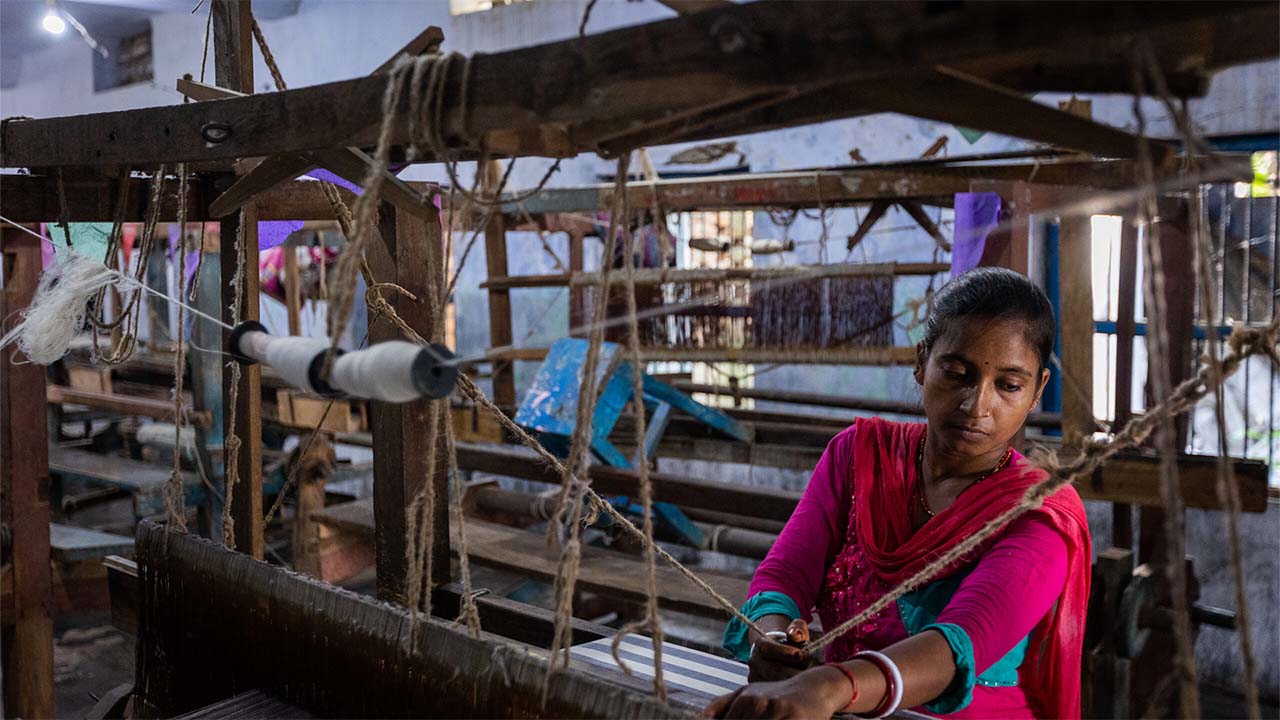

Former US First Lady Michelle Obama once famously said, “There is no limit to what we, as women, can accomplish.” Women often possess an innate ability to navigate adversity and emerge stronger. Lakshmi Amol Shinde from Wardha, Maharashtra, exemplifies this resilience. Leveraging her expertise in papad making and fueled by entrepreneurial drive, Lakshmi approached a self-help group to secure a business loan. Launching her papad venture in 2017, Lakshmi inspired eleven other women from her group to join her thriving business. Starting by selling products in her village, she has since expanded her enterprise to several cities in Maharashtra. From struggling to contribute INR 5,000 towards household expenses, Lakshmi now proudly provides INR 15,000.
Lakshmi’s story is just one example of rural women entrepreneurship in 21st-century India. Our nation boasts remarkable diversity, reflected in the myriad forms of entrepreneurship pursued by women. The availability of public and private microfinance, along with the support of self-help groups and initiatives like the National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM), has bolstered women’s empowerment and entrepreneurship. These efforts span various sectors, including health, clean energy, zero waste, education, women’s hygiene, garments, textiles, and services.
Rural entrepreneurship has emerged as a catalyst for economic empowerment among women in India’s hinterlands. For rural women, entrepreneurship represents not only a means to improve their economic status but also a path to personal empowerment and transformation. The rise of rural entrepreneurship has expanded opportunities and broadened perspectives for women across various fields.
Studies on rural entrepreneurship suggest that India’s GDP could increase by $0.7 trillion by 2025 through women’s participation in entrepreneurial activities and other economic endeavours. Despite government efforts to promote rural entrepreneurship and skill development through initiatives like Make in India and Standup India, only 14% of women in India engage in entrepreneurship, as per the Seventh Economic Census, 2019.
While many Indian women, like Lakshmi, aspire to entrepreneurship, they often face significant challenges in achieving success. India is among countries where female business owners encounter various hurdles, including cultural biases and limited access to business resources.
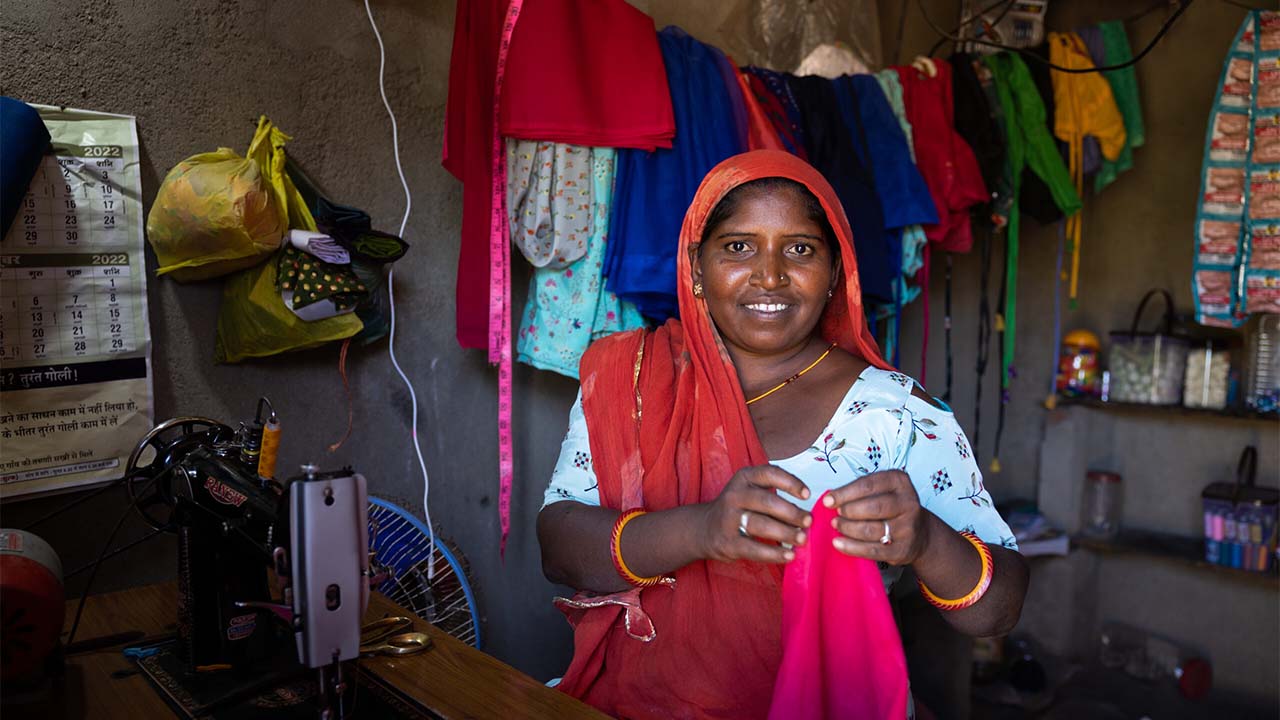

For rural women entrepreneurs, the gender gap is even more pronounced. In addition to cultural barriers, they contend with obstacles such as inadequate exposure to entrepreneurial skills, limited awareness of technology, scarce access to funding, and the challenge of balancing business responsibilities with family obligations. According to Innoven Capital, the percentage of funded startups with at least one female co-founder decreased from 17% in 2018 to 12% in 2019. Market access presents another hurdle, as women entrepreneurs encounter difficulties in effectively marketing their products.
Empowering women through education, skill development, and access to financial resources can foster a robust network of rural enterprises, contributing to the overall economy. Mentorship programs can also play a pivotal role in assisting rural women in overcoming barriers and establishing successful ventures. Women’s self-help groups and cooperatives hold potential in organising women into small groups, providing guidance on accessing capital, navigating government policies, and imparting the tools and skills necessary for entrepreneurial success.
Milestones, lessons, and the work already underway at MIF

Marico and Marico Innovation Foundation (MIF) reflect on ten years of Startup India and the diversity shaping India’s next phase of innovations.

Insights, impact, and execution: what it takes to turn ideas into solutions that serve people.

Get insights from entrepreneurs, investors, and change-makers on innovation,
success and what it takes to get there.
